What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a broad term encompassing all things that can connect to the internet and “talk” to each other, allowing connectivity between the physical and digital worlds.
The “things” in IoT refers to autonomous electromechanical devices with measuring, computing and connectivity capabilities. These ‘things’ transfer data about their current internal and external state.
The internet cloud acts as a “brain” consisting of automated software platforms that host value-added services, perform data analytics and provide a user interface to directly interact with you and me.
The combination of the internet and “things” in IoT allows large volumes of data to be gathered, analysed and enables suitable corresponding actions to be created.
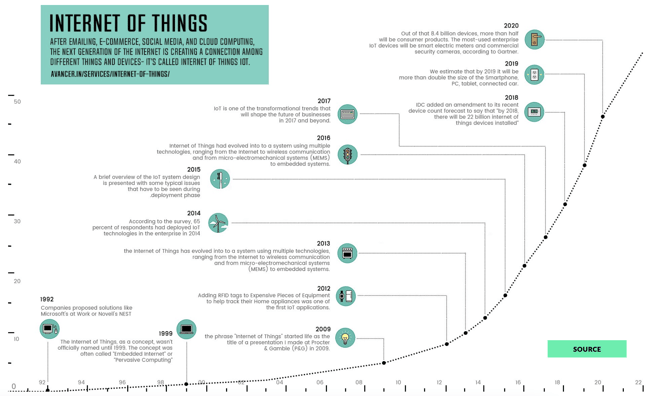
History of IoT
What is the key megatrend enabled by IoT?
At the heart of all things IoT is one common factor; Global connectivity.
Global connectivity means not only connecting the 7.8 billion people across the world but also the 10s of billions of devices making up the fundamental infrastructure of our global society.
However, these hyper connected devices also represent a major challenge, one that is being solved, thanks to the Internet of Things (IoT). The underlying communication and digital services industries, intrinsic to the development of global connectivity, are morphing, propelled by growth in fixed and mobile broadband penetration rates, alongside unprecedented innovation in software and smart devices.
Now once-inert consumer devices that were unconnected parts of our everyday lives are becoming ‘smart’, connecting to the internet’s network of networks and communicating with each other, acting as the bedrock for a rapidly digitalising economy.
Global connectivity and policy
Global connectivity is high on the policy agenda of most countries and global development and financial institutions, but why are such vast sums being spent, why is it important to enhance connectivity?
Succinctly, global connectivity increases the flow of goods, information and finance allowing both the promotion of growth and productivity, while enhancing access to geographically impregnable markets and untapped opportunities.
For companies wanting to expand their reach, global connectivity is essential.
To illustrate the point, the healthcare, energy and transport industries operate internationally and involve perishables requiring carefully controlled environmental conditions.
While these industries may want to expand internationally, this reach is uneconomical if it comes at the expense of product inventory.
IoT device sensors connect to the internet and provide the solution with real-time asset monitoring and management to ensure environmental consistency and process security, wherever you or the assets are in the world.
IoT Trends, industry focus
1. Transport and logistics
IoT is integral in the conventional tracking of fleets, which lead to dynamic fleet optimisation, reducing operational costs and delivering far superior monitoring of product assets in commercial transport for a wide variety of industries.
IoT Use Case: Cold-Chain Monitoring
A Cold-chain is a temperature-controlled supply chain made up of production, storage and distribution activities.
Monitoring of this cold chain encompasses associated equipment and logistics, which maintain and monitor the assets’ carefully controlled environmental conditions.
Recently, the demand for cold chain monitoring software solutions, such as reporting, data analytics, and tracking software, has increased considerably.
The software provides the ability to uninterruptedly monitor the performance of cold chains in real-time and ensure adherence to guidelines set by regulatory agencies such as the Food & Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organization (WHO). Of course, all of this software relies on IoT device sensors to provide large amounts of real-time data.

2. Healthcare and research
IoT applications such as telehealth, digital diagnostics, and remote monitoring make it possible for healthcare professionals to have better insight and real-time tracking of patients, leading to more proactive and the best possible treatment for patients.
IoT Use case: Cryogenic Equipment
Cryogenic equipment is used to generate, sustain or operate at extremely low temperatures.
In comparison to refrigeration, cryogenics operates at -153°C to absolute zero (-273°C). Offerings include tanks, valves, vaporizers and pumps.
There is an increased demand for cryogenic equipment throughout the world largely driven by improving healthcare services and increasing demand for liquid natural gas across the world.
Cryogenic equipment is a necessity in healthcare and research because many biological samples and pharmaceuticals must be maintained at very low carefully controlled temperatures, equipment that is especially pertinent in the development of a COVID-19 vaccine.
Until very recently, IoT has not played much of a role in cryogenics but now Quantum Cryogenics has revolutionized that with a new state-of-the-art IoT cryogenic monitoring solution.
3. Energy
Growing concerns in energy management have led to 2020 seeing the highest number yet of developmental projects in areas such as energy distribution, grid optimisation, remote asset monitoring and predictive maintenance.
IoT Use case: Gas Monitoring
Gas monitoring relies on the detection of any hazardous gas leaks, oxygen depletion or the presence of emissions (toxic or flammable gases). Technological advancements such as wireless communication facilities and sensor technologies are expected to drive market growth.
Additionally, as the cost of IoT sensors declines, a majority of the industries that deal with hazardous/flammable materials are likely to integrate these sensors into their day-to-day operations, to improve safety and operational efficiency. (Source)
4. Manufacturing
Employing a network of sensors enables the collection of critical production data and condition-based maintenance alerts; and also, using Cloud technology to turn this data into valuable insights about the efficiency of the manufacturing operations; IoT has drastically disrupted traditional manufacturing and began connecting previously disconnected assets.
According to Markets and Markets; the global IoT in manufacturing market size is expected to grow from USD 33.2 billion in 2020 to USD 53.8 billion in 2025, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 10.1% during the forecast period.
The major factors driving the growth of the IoT in the manufacturing market include:
- A rapidly increasing demand for automation of industrial processes within the manufacturing industry.
- A growing need for centralized monitoring and predictive maintenance of assets and resources.
- The exponential increase of cost-effective and intelligent connected devices and sensors, the growing need for reliable, secure, and high-speed network connectivity.
- The increased adoption of cloud computing platforms.
With the help of IoT, manufacturers are able to significantly improve the overall speed of production, improve the product quality as well as make the manufacturing process more cost-efficient.
According to Markets and Markets research, manufacturers are expected to invest up to $45.3B in IoT implementation by 2022. These figures have increased from $12,7B back in 2017 - a testament to just how rapidly the industry has been evolving and adopting new technologies as the world adjusts to sudden changes imposed by eventualities such as the coronavirus outbreak.

5. Location data will become more prominent
In 2020, due to the coronavirus pandemic prompting many retailers and other businesses to shift to things like curbside pickup and remote check-in; location data that is driven by IoT has never been more important.
The IoT in the manufacturing market by solutions is segmented into network management, data management, device management, application management, and smart surveillance.
With Analytics for IoT, users can configure feeds and ingest streaming data to immediately visualize real-time information in web maps and dashboards.
IoT analytics include some of the necessary tools needed to perform some of the following tasks:
- Analyzing patterns in daily processes and operations.
- Finding locations of both damages, inconsistencies or errors.
- Managing company operations data with ease.
- Summarizing data from all data points and creating easy to understand graphical visualizations.
- Data enrichment to assist key stakeholders to make better-informed decisions with both foresight and hindsight data to guide decision making.
6. Automated data centres
With the workflow of data centres disrupted by lockdown restrictions, companies are looking to public cloud solutions to cope with the rising demand from the work-from-home user. IoT can help optimize client data flow, security, storage requirements, and access capabilities.
The COVID-19 pandemic has already begun to drive innovation in data center operations, forcing companies to embrace automation to manage some duties that currently rely on close human interaction for their execution.
Software and robotics will play larger roles in aspects of operations, and contactless, “lights out” strategies will gain new urgency in maintaining existing mission-critical facilities and building new ones.
Thanks to Artificial intelligence technology, facility automation has rapidly accelerated in all industries and holds the promise of automating entire infrastructure, requiring the presence of human interaction less and less by the day.
Understanding the impact of COVID-19 on IoT
In the short term, the current economic uncertainty has constrained the demand and funding for many IoT-related projects, with some businesses seeing a drop of around 50% in new order intake.
However, in the long-term COVID-19 has brought about a digital transformation, and a permanent shift leading to the accelerated adoption of various technologies such as IoT, by people, governments, and businesses across the globe.
The COVID-19 virus is undoubtedly a tragedy, it is also true to say that if it happened to us at any other point in history, the death toll and economic devastation would have been greatly amplified.
IoT technology breakthroughs are changing the world:
- Medical research scientists can react more rapidly, with greater molecular precision, and in a coordinated effort to develop a vaccine.
- E-commerce has the logistical infrastructure to replace physical stores and the internet can handle sustainably high traffic.
- Enterprises can implement digital transformation with far greater ease, turning an arduous project, lasting years, into weeks.
Many of these breakthroughs are enabled by IoT technology, with many use cases coming into a much sharper focus.
- In healthcare, patient data collection and connected hospitals have assumed greater importance.
- Going forwards there will be a need for IoT technology in the logistical management of vaccine rollout globally, with a requirement for carefully monitored and controlled environmental conditions.
Across industries, IoT solutions that enable remote working and monitoring can help businesses recover and thrive in the future.
How Quantum is innovating with IoT technology
Quantum Cryogenics’ technology, including gas detection, cryogenics and logistics monitoring, has been at the forefront of the industry; cutting across sectors including healthcare, energy and transport.
Connectivity is the future. That is why we are launching smart technology that is ready to meet industry-specific needs within a highly connected world.
Sophisticated device sensors are integrated into all of our product lines to transmit data to our state-of-the-art IoT CryoHub software enables us all to work, and work together.
At Quantum Cryogenics our mission is to keep your people, assets and technology safe through globally connected smart monitoring solutions, and with our latest IoT technologies, we will be able to do just that.
.png)